
What does an atomic bomb have to do with energy generation?
Splitting atoms releases enormous amounts of energy. To be useful rather than destructive, nuclear power plants must be safeguarded, but this attempt is not always successful.
Nuclear Energy
When the nucleus of an atom is split, it releases a huge amount of energy called nuclear energy. For nuclear energy to be used as a power source, scientists and engineers have learned to split nuclei and to control the release of energy (Figure below)
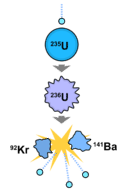
When struck by a tiny particle, Uranium-235 breaks apart and releases energy.
Nuclear Energy Use
Nuclear power plants, such as the one seen in Figure below, use uranium, which is mined, processed, and then concentrated into fuel rods. When the uranium atoms in the fuel rods are hit by other extremely tiny particles, they split apart. The number of tiny particles allowed to hit the fuel rods needs to be controlled, or they would cause a dangerous explosion. The energy from a nuclear power plant heats water, which creates steam and causes a turbine to spin. The spinning turbine turns a generator, which in turn produces electricity.

Nuclear power plants like this one provide France with almost 80% of its electricity.
Many countries around the world use nuclear energy as a source of electricity. In the United States, a little less than 20% of electricity comes from nuclear energy.
Consequences of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is clean. It does not pollute the air. However, the use of nuclear energy does create other environmental problems. Uranium must be mined (Figure below). The process of splitting atoms creates radioactive waste, which remains dangerous for thousands or hundreds of thousands of years. As yet, there is no long-term solution for storing this waste.

Uranium mine in Kakadu National Park, Australia.
The development of nuclear power plants has been on hold for three decades. Accidents at Three Mile Island and Chernobyl, Ukraine verified people’s worst fears about the dangers of harnessing nuclear power (Figure below).

Damaged building near the site of the Chernobyl disaster.
Recently, nuclear power appeared to be making a comeback as society looked for alternatives to fossil fuels. After all, nuclear power emits no pollutants, including no greenhouse gases. But the 2011 disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan may have resulted in a new fear of nuclear power. The cause of the disaster was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake and subsequent tsunami, which compromised the plant. Although a total meltdown was averted, the plant experienced multiple partial meltdowns, core breaches, radiation releases, and cooling failures. The plant is scheduled for a complete cold shutdown before the end of 2011.
Nuclear power is a controversial subject in California and most other places. Nuclear power has no pollutants including carbon emissions, but power plants are not always safe and the long-term disposal of wastes is a problem that has not yet been solved. The future of nuclear power is murky.
Summary
Nuclear power plants use uranium in fuel rods, which later become nuclear waste. Nuclear waste can be dangerous for hundreds of thousands of years.
Periodic accidents involving nuclear power plants seem to slow down the development of nuclear power in many countries.

No comments:
Post a Comment